Last updated: March 24, 2025
Article
Synthesis of Studies on the Effects of Artificial Light at Night
1978-2024, with 2024 update
Project Summary
The Natural Sounds and Night Skies Division (NSNSD), within the Natural Resource Stewardship and Science Directorate (NRSS), develops, uses, and distributes the tools of natural and social science to help the National Park Service (NPS) fulfill its core mission: to protect park resources and values. As part of this, NSNSD strives to be aware of, understand, and communicate current scientific knowledge in our fields particularly as pertains to work that can help inform management of resources and the visitor experience. However, it can be challenging to stay abreast of scientific topics experiencing rapid growth in knowledge. This project addresses this challenge by conducting systematic, comprehensive, up-to-date queries and summaries of the scientific literature.
Changes in the nocturnal environment – arising from expansion of human populations, urban areas, transportation networks, and resource extraction activities – are a global issue1 with implications for human health and ecosystem integrity2 (Figure 1). An increasing body of scientific literature is documenting the effects of artificial light at night (ALAN) on species and ecosystems, with findings that are useful for resource management3. This project summarizes the results from our systematic query of the literature, with the intent to provide park managers with an updated understanding of the relevant scientific knowledge.
Notably, our approach is distinct from the results from an ad hoc query using Google Scholar or a related tool. We developed, tested, reviewed, and improved our query through an iterative process to ensure that the results encompass all the relevant literature. Though no tool can guarantee it will capture every relevant paper, our current process delivers results that are far more comprehensive than mere searches or less systematic queries.

Finding Relevant Studies
In 2018, we established a peer-reviewed literature search using Thompson’s ISI Web of Science (WOS). We tested the results against an established list of relevant papers on the effects of artificial light at night, capturing 92% of known studies using our search criteria.
Since then, we have conducted yearly literature searches following the same protocol, up to and including 2024. A subject matter expert reviews all papers identified by the search, to ensure that we include only studies documenting the ecological or health effects of artificial light at night in the final data set (N = 618 relevant studies from 1978 to 2024). Irrelevant papers include those that summarize light levels without documenting a response. For the papers deemed relevant, the subject matter expert labels each paper with a light source category (e.g., transportation, resource extraction) and effect category (e.g., human, wildlife). Additionally, we use automated searches to identify key words that appear in publication titles (e.g., sleep, bats, turtles, insects).
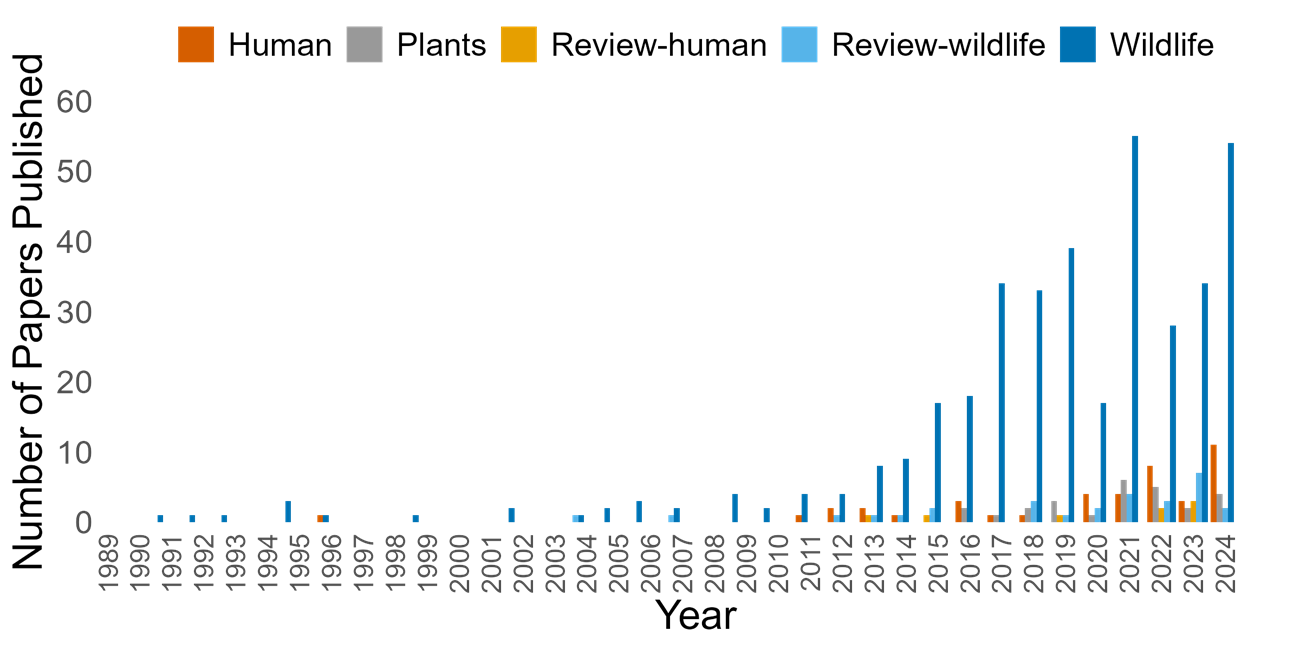
Number of Studies 1978-2024
Even though our literature search began in 1978, the first relevant papers on the effects of light on wildlife only date back to 1991 and, for humans, 1995. Our query did find some laboratory studies pre-1991, but we do not include these in Figure 2. For wildlife, the number of studies published each year has increased noticeably since 2011 (Figure 2). For humans, few studies were available before 2011. In 2016, the first studies on the effects of artificial light at night on plants were published. Papers documenting effects of light on wildlife, particularly marine species and ecosystems, continue to be more common than other ALAN-related research topics in 2024.
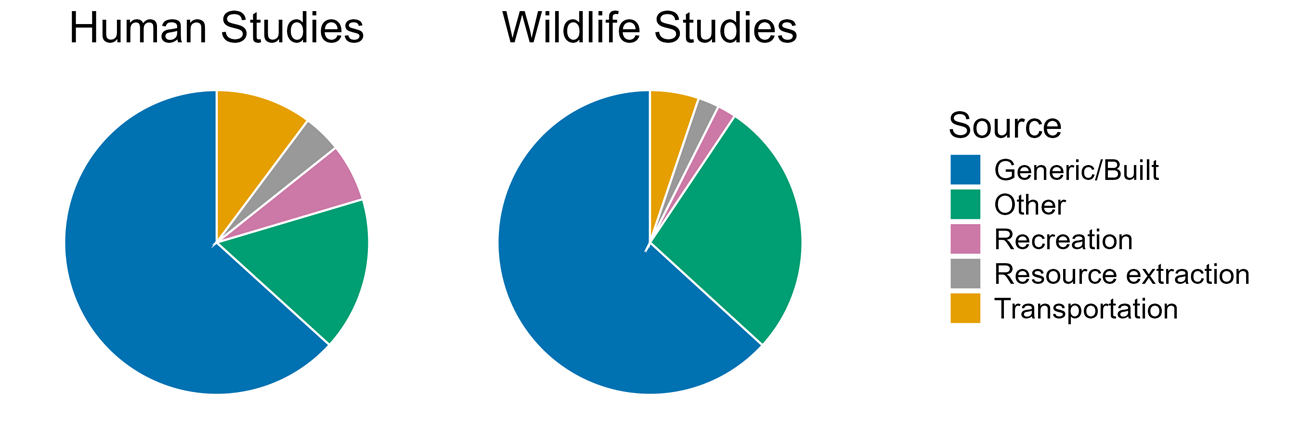
Sources of Artificial Light at Night, 1978-2024
A subject matter expert labeled all relevant papers with a category of light source: light from built environment (all sources together), transportation, recreation, resource extraction (which included industrial sources), military, or other (Figure 3). The "other" category includes studies where light was added in an experimental setting. We did not find any studies where multiple sources were investigated. Most of the human and wildlife studies are focused on light from the built environment.
Keyword Trends from 1978 to 2024
In the 50 studies on human response to light, 10 studies looked at the effect on sleep, and 5 of the studies looked specifically at the effects of street lighting. One study, A laboratory study of the psychological impact of light pollution in national parks (Benfield et al. 2018), had direct implications for management of lights in park settings.
In the 407 studies on wildlife response to artificial light, article titles contained the following keywords:
- 61 on birds
- 26 on turtles
- 28 on insects
- 37 on bats
- 26 on plants
- 3 studies in parks or protected areas

Trends in Topics, 1978 - 2024
To examine different topics discussed in the literature, we generated word clouds for wildlife studies from the titles and abstracts for all publications (1978-2024).
The animated GIF below shows word clouds of topic trends for wildlife publications from 1990-1999, 2000-2009, 2010-2019, and 2020-2024. Early wildlife publications focused on turtle hatchlings, while later studies included more diverse taxa (e.g., bats, insects, fish). In the GIF, the term “alan” is the acronym for “artificial light at night”. Human studies were not included in this analysis because of the low number of publications on a decadal scale.
2024 Update
The search for publications in 2024 produced 77 papers deemed relevant by a subject matter expert. There were 11 new studies on humans (0 of which were reviews), and 56 new studies on wildlife (2 of which were reviews). (Additional studies were laboratory studies, which are not described in this summary.)
In the 56 studies on wildlife response to artificial light at night, article titles contained the following keywords:
- 4 on bats
- 2 on insects
- 4 on birds
- 4 on plants
- 2 on turtles
- 0 studies in parks or protected areas
Suggested Reading
While the bulk of papers published in 2024 continued to investigate the effects of light on species and ecosystems or document the expansion of light pollution in developing regions, several stand out for their unusual or unexpected conclusions:
-
Light pollution affects not only plants and animals, but can even alter soils.
Li, Hu, & Chen (2024) found that artificial light at night (ALAN) destabilized bacterial networks in soil, favoring light-tolerant species, increasing species interdependencies, and reducing the abundance of denitrifiers (bacteria that convert nitrate NO3- into atmospheric N2.
-
Behavioral reactions to light can be passed to future generations (at least, among zebrafish).
It’s already well-known that numerous species change our behavior and/or experience physiological changes when we’re exposed to artificial light, particularly bright, short-wavelength blue-white lights. (Some species can’t see longer-wavelength red or amber light as well as humans do, so it doesn’t bother them as much.) But now, Li, Zhang et al. (2024) have found not only that zebrafish are more anxious when repeatedly exposed to short wavelength lights, but also that offspring of zebrafish exposed to any artificial light at night (ALAN) continue to be more hesitant and jittery than a control group, even when they don’t experience the light themselves.
-
The economic loss in global ecosystem services due to light pollution totals a whopping $3.4 trillion per year.
While excess or unwanted artificial light is already a waste of energy, its ecological impacts also come with a price tag. Anderson et al. (2024) used global models of light pollution to estimate degradation of ecosystem services (the benefits that ecosystems provide for human well-being, such as harvestable fish from healthy marine environments or pollination by birds, bats, and insects). They found that the losses totaled 3.4 trillion U.S. dollars!
-
The rare upside to light pollution! Artificial light affects pests and disease vectors such as the Asian tiger mosquito and southern multimammate mouse, perhaps inhibiting their growth in bright urban areas.
Artificial light can confuse, disturb, and disorient a wide array of species. Usually, this is ecologically harmful. However, it can also negatively affect species that cause disease or destruction. For example, Qing et al. (2024) found that artificial light at night tricks Asian tiger mosquitoes – which can host or transmit dengue fever, zika, and other diseases – into thinking that days aren’t getting shorter, so they don’t adapt properly to the onset of winter and colder temperatures. Meanwhile, Oosthuizen et al. (2024) verified that the African nocturnal rodent called the southern multimammate mouse – also a vector for pathogens, as well as an agricultural pest – decreased their activity by up to 75% when exposed to light at night.
- Li, XM; Hu, HF; Chen, SC. (2024). Artificial light at night causes community instability of bacterial community in urban soils. Science of The Total Environment 921: 171129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.171129. Open Access.
- Li, WW; Zhang, DX; Zou, QQ; Bose, APH; Jordan, A; McCallum, ES; Bao, JH; Duan, M. (2024). Behavioural and transgenerational effects of artificial light at night (ALAN) of varying spectral compositions in zebrafish. Science of The Total Environment 954: 176336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.176336
- Anderson, SJ; Kubiszewski, I; Sutton, PC. (2024). The Ecological Economics of Light Pollution: Impacts on Ecosystem Service Value. Remote Sensing: 16 (14), 2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs16142591 Open Access.
- L. Qing, Heng-Duan Zhang, Dan Xing, Jing-Wen Xie, Yu-Tong Du, Ming Wang, Zi-Ge Yin, Nan Jia, Chun-Xiao Li, Teng Zhao, Yu-Ting Jiang, Yan-De Dong, Xiao-Xia Guo, Xin-Yu Zhou, Tong-Yan Zhao. (2024). The effect of artificial light at night (ALAN) on the characteristics of diapause of Aedes albopictus. Science of The Total Environment 924: 171594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.171594. Open Access.
- Oosthuizen T., N. Pillay, M. K. Oosthuizen. (2024). A mouse in the spotlight: Response capacity to artificial light at night in a rodent pest species, the southern multimammate mouse (Mastomys coucha). Journal of Environmental Management 372: 123373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.123373. Open Access.
Where to Find More Information
A searchable spreadsheet of all the relevant studies is available upon request (see contact information below). The spreadsheet will be updated annually. In most cases, NSNSD staff has access to the full text of the publications and can share a link, email a pdf, or assist in finding the reference.
For a summary of past suggested reading, please click here [Word doc, 22 KB].
Project Contacts
Cathleen Balantic, PhD. Tyra Olstad, PhD. Natural Resource Stewardship and Science Directorate, Natural Sounds and Night Skies Division. Email: SoundscapeSupport@nps.gov
References
1 Falchi, F., Cinzano, P., Duriscoe, D., Kyba, C. C., Elvidge, C. D., Baugh, K., … & Furgoni, R. (2016). The new world atlas of artificial night sky brightness. Science Advances, 2(6), e1600377.2 Longcore, T., and C. Rich. 2016. Artificial night lighting and protected lands: ecological effects and management approaches. Natural Resource Report NPS/NRSS/NSNS/NRR—2016/1213. National Park Service, Fort Collins, Colorado, 51 pp.
3 Seymoure BM, Buxton R, White J, Linares C, Fristrup K, Crooks K, Wittemyer G & Angeloni L. 2025. Global light pollution masks natural light cycles and affects numerous species. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment. https://doi.org/10.1002/fee.2832
4 Cinzano, P., Elvidge C. 2003. Night sky brightness at sites from satellite data. Memorie della Società Astronomica Italiana, 74, 456-457.
